The ekip project
This is where ekip (European Cultural and Creative Industries Innovation Policy Platform) comes in, a project funded by the European Union under the Horizon Europe programme. The project, led by Charlotte Lorentz Hjorth from Lund University, is coordinated for the Design Department by Valentina Auricchio with Vanessa Monna and Luisa Maria Virginia Collina, and involves many other researchers from the Department: Stefana Maja Broadbent, Chiara Colombi, Andrea Giuseppe Manciaracina, Silvia D'Ambrosio, Marzia Mortati, Silvia Deborah Ferraris, Paola Bertola, Erminia D’Itria and Francesco Zurlo.
The aim of ekip is to support the development of policies that establish open innovation processes as a new standard, ensuring that support ecosystems can cultivate the capacity to manage complex multi-stakeholder innovation processes. These processes are essential for achieving greater innovation within European CCIs and driving behavioural change towards a greener, more inclusive and digital Europe.
The ekip Observatory
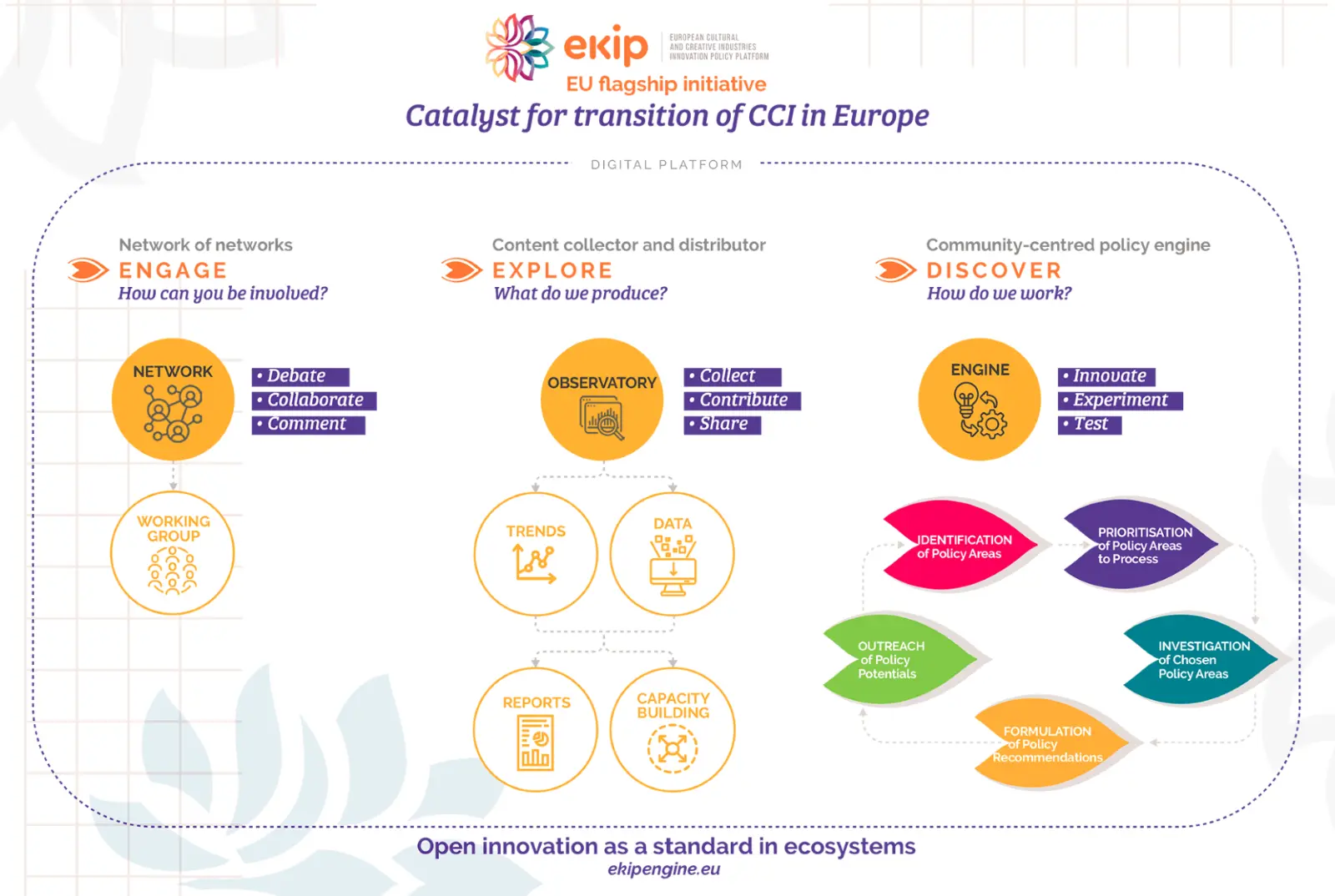
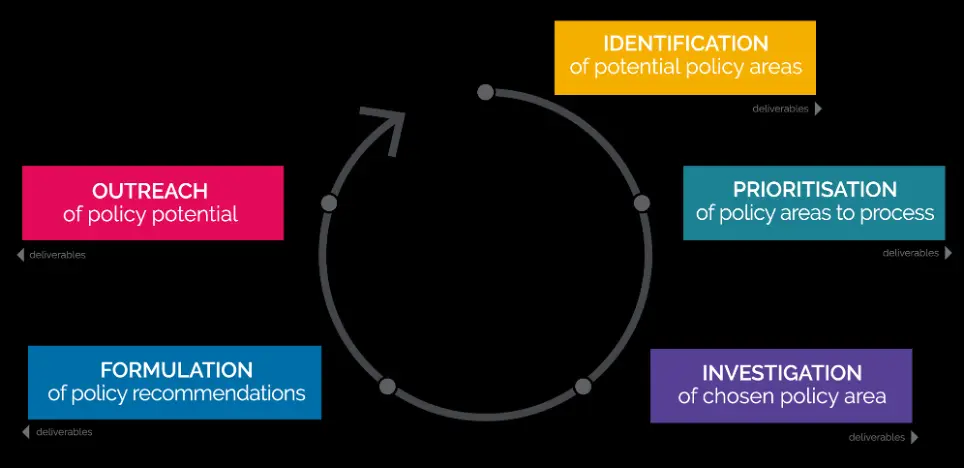
As of 1 June 2023, the Design Department of the Politecnico di Milano is responsible for the development of the ekip Observatory, a new digital platform for innovation policies for CCIs. The ekip Observatory acts as a central interface for the dissemination of innovation policies and as a repository for knowledge production, integrating the Knowledge Bank and providing policy recommendations based on concrete data.
Functions and Activities of the ekip Observatory:
Digital Platform: The platform communicates results and ensures stakeholder engagement through knowledge sharing.
- Data Collection: Uses social media listening, trend forecasting and desk research techniques to understand the needs and profiles of CCI users.
- Knowledge Translation: Converts collected data into communicative formats such as graphs and infographics for wider and more accessible dissemination.
- Policy Recommendations Mapping: Collection and analysis of over 354 policy recommendations from EU-funded projects to create an accessible repository for stakeholders.